In recent years, technological advancements have opened new avenues for enhancing accessibility for individuals with visual impairments. One notable innovation is “Robbie,” an AI-powered robotic guide dog developed by Scottish engineers. Designed to assist visually impaired individuals in navigating indoor spaces, Robbie represents a significant stride toward addressing the challenges associated with traditional guide dog availability and training.
The Genesis of Robbie
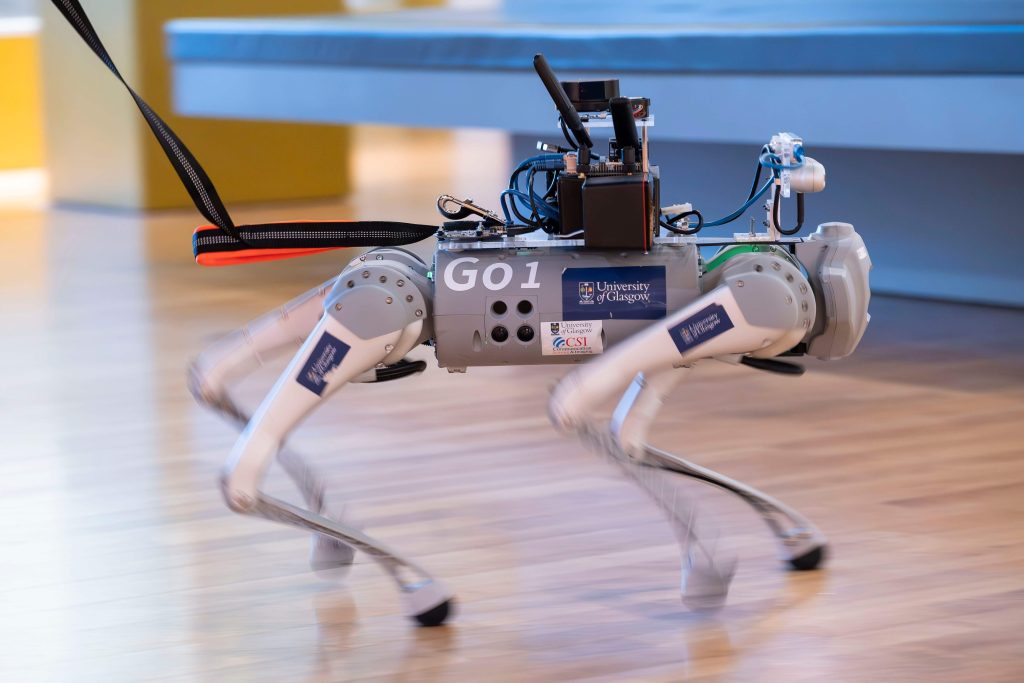
Robbie’s development is spearheaded by a team at the University of Glasgow, led by Dr. Wasim Ahmad from the James Watt School of Engineering. The project aims to create a cost-effective and efficient alternative to traditional guide dogs, which require extensive training and resources. The inspiration behind Robbie stems from the need to provide immediate assistance to those awaiting guide dogs and to offer support in environments where traditional guide dogs may not be practical.
Technological Framework
Robbie is equipped with advanced artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, enabling it to autonomously navigate complex indoor environments. The robot utilizes a combination of 3D scanners and cameras to perceive its surroundings, allowing it to detect obstacles and plan safe paths for the user. This sensory integration ensures that Robbie can adapt to dynamic environments, making real-time decisions to guide users effectively.
One of the standout features of Robbie is its conversational AI capabilities. The robot can engage in interactive dialogues with users, providing information about the environment, describing nearby objects, and even reading product labels in settings like supermarkets. This level of interaction not only enhances the user’s situational awareness but also fosters a sense of companionship, addressing the emotional aspects of assistance.
Economic and Practical Considerations
The cost implications of training and maintaining traditional guide dogs are substantial, often reaching up to £38,000 per dog. In contrast, Robbie’s production costs are approximately £12,000, presenting a more affordable solution for many individuals and organizations. Additionally, the scalability of robotic guide dogs like Robbie means that they can be deployed in various settings without the logistical challenges associated with live animals. The Scottish Sun
User Feedback and Trials
Robbie has undergone extensive trials in collaboration with the Royal National Institute of Blind People (RNIB) Scotland. These trials involved participants navigating through environments such as museums and shopping centers, guided by Robbie. The feedback has been overwhelmingly positive, with users expressing appreciation for Robbie’s responsiveness and the sense of independence it provides. Eight out of ten participants in a recent trial reported a favorable experience, highlighting Robbie’s potential to complement traditional guide dogs.
Global Perspectives on Robotic Guide Dogs
The development of robotic guide dogs is not confined to Scotland. Researchers worldwide are exploring similar technologies to enhance mobility for visually impaired individuals. For instance, a team at Binghamton University in New York has programmed a robot to respond to leash tugs, mimicking the behavior of traditional guide dogs. In China, researchers have tested a six-legged robot designed to assist with navigation, showcasing the global interest in robotic assistance for the visually impaired.

Challenges and Future Directions
While Robbie represents a significant advancement, several challenges remain. One primary concern is the robot’s current limitation to indoor environments. Navigating outdoor settings introduces variables such as weather conditions, uneven terrains, and complex traffic scenarios, which require further technological developments. Moreover, the emotional bond between humans and animals is profound, and while Robbie offers companionship through interaction, it cannot entirely replicate the unique relationship shared with a living guide dog.
Future iterations of robotic guide dogs aim to address these challenges by enhancing sensory capabilities for outdoor navigation and improving interactive features to better emulate the companionship provided by traditional guide dogs. Collaboration with visually impaired communities is crucial to ensure that these technologies meet user needs and preferences effectively.
Ethical and Social Implications
The integration of AI-powered robotic guide dogs into society raises important ethical and social considerations. Ensuring accessibility and affordability is paramount to prevent widening the gap between those who can and cannot afford such technologies. Additionally, addressing concerns about data privacy and security is essential, given the extensive sensory data these robots collect during operation.

Robbie, the AI-powered robotic guide dog, signifies a transformative approach to enhancing accessibility for visually impaired individuals. By leveraging advanced technologies, Robbie offers a practical and cost-effective supplement to traditional guide dogs, addressing shortages and providing immediate assistance. As research and development continue, it is imperative to consider the diverse needs of users, ensuring that such innovations are inclusive, ethical, and truly beneficial to the communities they aim to serve.
The journey of integrating robotic guide dogs like Robbie into daily life is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of solutions that empower individuals, fostering independence and improving quality of life.
Copyright©dhaka.ai
tags: Artificial Intelligence, Ai, Dhaka Ai, Ai In Bangladesh, Ai In Dhaka, Robbie



